Article • 9 min read
A guide to building a knowledge base (+3 best practices)
Deliver exceptional service and form deeper connections with your customers by building a knowledge base.
Por Stella Inabo, Contributing Writer
Última atualização em March 27, 2024
As a business grows, more support tickets tend to come in. Many customers ask the same basic questions, while others have complex queries. Through it all, support agents must proactively address issues and maintain a high level of service. But when ticket volume increases, so do agents’ stress levels.
Sound like your company? If so, here’s the good news: building a knowledge base can help stem the tide and keep your support staff afloat. A knowledge base can also make for better customer experiences. In fact, 69 percent of buyers want to resolve as many issues as possible on their own, according to the Zendesk Customer Experience Trends Report.
69% of buyers want to resolve as many issues as possible on their own.
Simply offering a standard knowledge base isn’t enough, though—the design of your help center affects your customers’ experience with your brand. When creating a knowledge base, it’s important to keep it simple, intuitive, and agile.
What is a knowledge base?
A knowledge base is a virtual library of information about your products or services. It can address everything from how to get started with your product to advanced troubleshooting inquiries.
Knowledge bases are an integral part of customer self-service, as visitors can use the resources to get the information they need on their own at any time. Agents can also streamline their workflows by directing customers to helpful articles or checking the knowledge base for answers to common questions.
What are the benefits of building a knowledge base?
A knowledge base empowers customers to help themselves during and after business hours. With knowledge base articles, customers can solve their own problems instead of reaching out to a support agent. Making it easy for buyers to find answers to their questions online reduces customer effort, decreases the number of support tickets, and keeps customers happy.
Your support team benefits from a well-designed knowledge base, too. Agents can quickly search through resources to find solutions to customer issues. And instead of writing out the answers themselves every time, agents can just send customers the link to an article that addresses their needs. With more time on their hands, agents can focus on resolving complex customer problems.
When you have a small number of customers, it’s feasible for your support staff to provide them with all the answers and attention they need. But as your company grows and your audience increases, the task becomes more difficult. A knowledge base management system enables you to deliver high-quality customer support at scale without burning out your agents.
How to create a knowledge base in 6 simple steps
Building your first knowledge base may seem confusing or overwhelming at the onset. You might be wondering what questions to include, how to answer them, and where to host the content. Follow these six steps to make the process easier to manage.
1. Determine which questions you want to answer
You might be faced with a large number of queries covering an array of different topics. Begin by identifying the questions that come up over and over again. Then, move on to the less common questions that still hone in on the challenges customers face.
To determine the most frequently asked questions, you’ll need to review support tickets. Manually checking tickets is cumbersome, so consider automating the process with a CRM that can spot and gather trends. You can also use a heat mapping tool like Hotjar to understand how users interact with your website and what obstacles they encounter.
Customer-facing teams (such as sales and support) may also have a sense of typical user issues. Set up meetings with staff from these departments to gather this information. Alternatively, team members could share what they know in a collaborative document that’s accessible to everyone.
2. Identify the optimal knowledge base structure
Customer questions likely cut across various aspects of your business, so you might not know exactly how to structure your knowledge base. The key is to design it in a way that makes it easy for visitors to find answers.
Your knowledge base structure will depend on your customers and your product or service. For example, at Zendesk, we categorize our knowledge base by solution because our customers often have product-specific questions.

Organizing questions by product might not work for a store or an ecommerce brand, as there are so many categories to cover. Instead, you might decide to answer queries about orders, returns, shipping, and products like Magnolia does.

Other things you should consider when designing your knowledge base are:
Adding a prominent search bar at the top of the page so customers can quickly find what they’re looking for
Placing FAQs in a location that’s easy to spot, preferably on the left-hand side of the page
Including a contact number, ideally at the bottom of the page, so customers can speak to support agents when they can’t get the answers they need from the knowledge base
3. Select your contributors
Knowledge base contributors should be team members who have regular contact with your customers, like support and sales reps. You might also involve non-customer-facing staff who have the specialized technical knowledge needed for troubleshooting, such as product managers and engineers.
If you’re a large company and you have the resources, consider creating a team solely focused on writing content for and updating the knowledge base.
4. Establish writing guidelines
Without a style guide, contributors may produce written content that sounds inconsistent and contains errors. Create a guide that sets clear standards for how to write and format knowledge base content.
To adopt a uniform voice, put writing rules in place. If you’re not sure where to start, here are some ideas:
Write in simple language. Avoid jargon and explain ideas like your readers are 10 years old.
Break up long blocks of text with white space.
Include illustrations, screenshots, and videos to describe concepts.
Add alt text to images to increase accessibility.
Optimize content for search by using keywords.
Consider using an editing tool like Grammarly to check the overall writing quality. Grammarly proofreads for errors, sharpens your sentences, helps you express ideas clearly, and detects structural problems.
5. Create the resources
While written content is more popular for a knowledge base, other mediums—like videos and screen recordings—are also useful for explaining complex processes. Consider tools like Loom or Vidyard to generate visual content. You may want to create infographics, diagrams, and illustrations as well.
Once you’ve chosen the type of content you’ll produce, set deadlines to hold contributors accountable. If you have many people working together, it’s best to appoint a leader with strong organizational skills who can ensure everyone does their part and submits content on time.
Watch a quick knowledge base demo
See how it's quick and easy to build a knowledge base with Zendesk.
6. Upload and publish your content
Knowledge base software makes it simple to upload content and review performance data. While the publication process will vary from software to software, the solution you choose should have these essential features:
A search engine that swiftly delivers the information your customers need
Feedback and analytics to help you understand how customers use your products and find areas for improvement
Content management capabilities that allow you to easily create, revise, schedule, and publish content on your knowledge base
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning technologies to streamline maintenance, surface relevant resources, and fill knowledge gaps
Best practices for setting up a knowledge base
As you build your first knowledge base, there are a few mistakes you’ll want to avoid. You don’t want to confuse your customers with jargon or make navigation a nightmare. You also don’t want to leave them with more questions than answers. Create an optimal knowledge base by following these knowledge management best practices.
Make complex knowledge simple to consume
A straightforward knowledge base design features intuitive navigation that makes it effortless to get answers—just what self-sufficient customers want.
Use clear, concise, and consistent categories to help customers find what they’re looking for quickly. Rakuten’s knowledge base is a good example. The company positions common tasks right below a prominent search bar so customers can surface the information they need. And on the left-hand side, Rakuten includes other help topics and a link to its Contact Us page.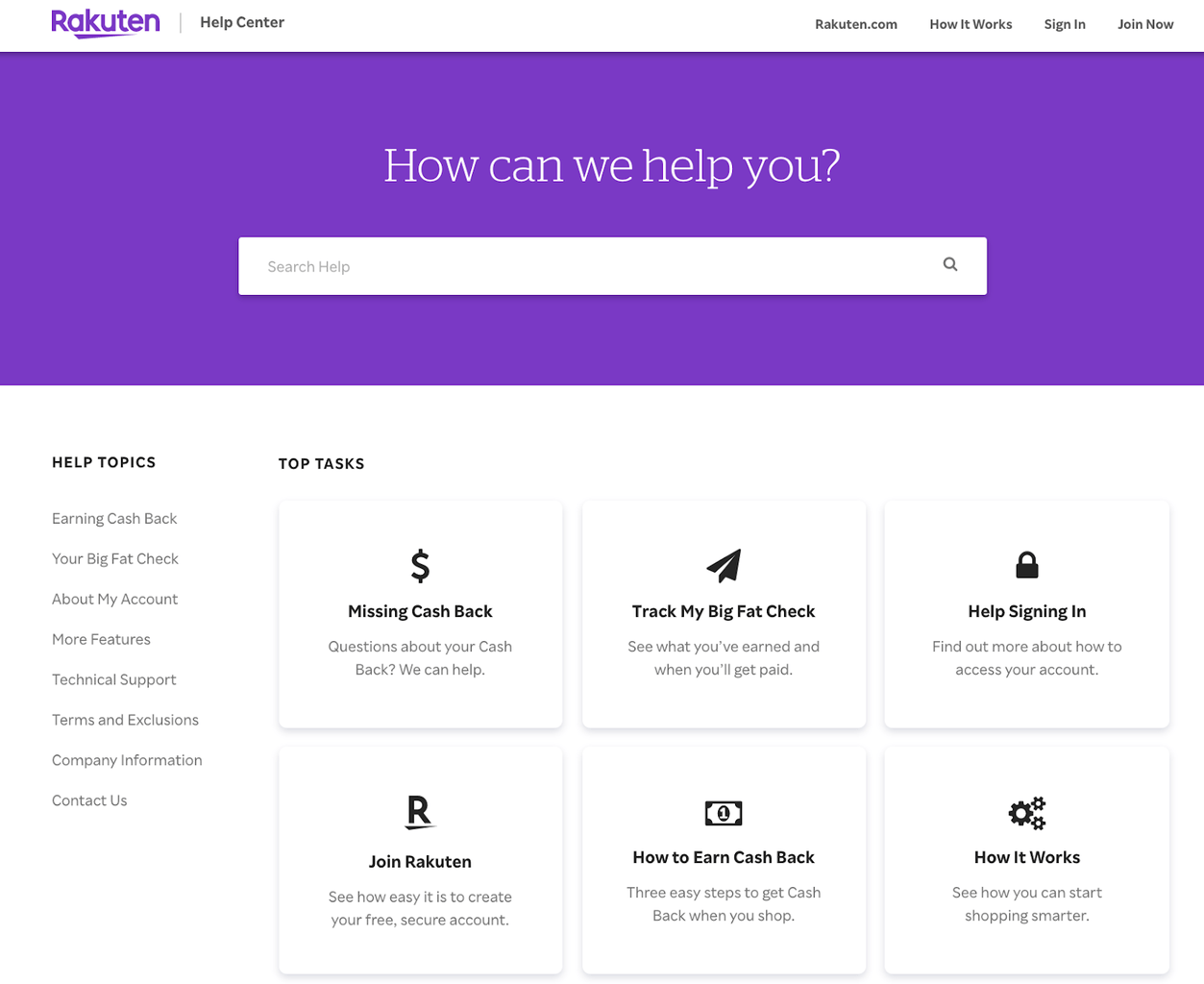
To make articles easy to discover, include keywords in titles so they show up in the search results. When crafting article titles, try to think about what a customer might search for. For example, a customer is more likely to type, “How can I report a stolen card” than “Reporting your lost card.”Design a highly tailored experience
Jam-packing your help center with information about every product and feature can overwhelm customers. If they can’t find content that’s relevant to them, they’ll give up and reach out to an agent instead.
Build product-specific help centers that address customer questions about your offerings. Ensure you add advanced search capabilities to help customers get answers as fast as possible. Place the search bar front and center so customers don’t need to look for it. You can also use an AI-powered chatbot to deliver knowledge base content based on the inquiry, the part of your website the visitor is interacting with, or where the customer is in the buyer journey.Use analytics and AI to detect trends and content gaps
Self-service analytics provide your support team with insights into the popularity, effectiveness, and pain points of your content. And a CRM with artificial intelligence enables your team to spot self-service trends that an individual support agent might miss. That data can help you understand the content gaps between your knowledge base articles and customers’ needs. You can then determine what to write next and where to improve existing knowledge.
Zendesk offers a Content Cues feature to surface trending topics. Our software uses machine learning technology and article usage data to help you identify common questions and keywords. It also alerts you when you need to review or improve an article.
Enable peer-to-peer support
Sometimes, customers have questions that are best posed to other customers. Build peer-to-peer support into your knowledge base to cultivate a community for your buyers—but note that this is only possible if your community forum is easily discoverable. For instance, Khan Academy prominently places its community as a category inside its help center.
In the community forum, Khan Academy users can get ideas from other parents on how to track student progress, ask questions about classes, and find quick tips to troubleshoot technical problems.
Maintain and improve your knowledge base
Designing your knowledge base shouldn’t be a one-time thing—a great knowledge base requires continuous improvement over time.
Start by creating a few articles that address the most common issues and questions, and then build on that content. Vet articles on a regular basis to ensure their relevance as your product and business evolve. Use metrics like page views and bounce rates to determine what content is helping customers and what needs to be improved.
With a well-maintained external knowledge base, you’ll be set to grow your community and build deeper connections with your customers.
